2.0 Configure new router using OpenZiti
In this section, we are describing how to setup the Edge Router (pub-er) for our test network.
2.1 Create the Edge Router VM
Please follow Create a VM section of the Controller Guide to setup a VM to be used as Router.
2.2 Login and Update the repo and apps on VM
- Azure
- AWS
- Google Cloud
- Once the VM is created, we can get the IP address of the VM from the Virtual machine screen.
- Login to the VM by using defined user "username" (default username is azureuser) and the private sshkey:
ssh -i <private_key> <username>@<ip>
- Once the VM is created, we can get the IP address of the VM from the Instance(s) screen.
Login to the VM by using user name "ubuntu":
ssh -i <private_key> ubuntu@<ip>
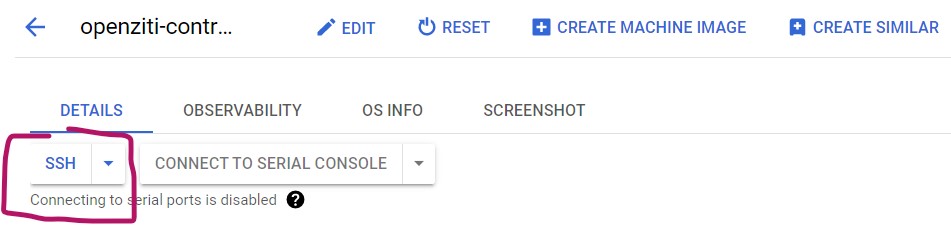
- Once the VM is created, we can login through SSH button on the VM instances screen. Make sure ssh is allow on the firewall before you do this. Alternatively, you can configure firewall first.
2.2.1 apt update
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
2.2.2 Download ziti_router_auto_enroll binary
ziti_router_auto_enroll is an easy way to setup your router automatically.
wget https://github.com/netfoundry/ziti_router_auto_enroll/releases/latest/download/ziti_router_auto_enroll.tar.gz
tar xf ziti_router_auto_enroll.tar.gz
You should have a file ziti_router_auto_enroll under the directory.
For detail info on ziti_router_auto_enroll, please checkout the ziti_router_auto_enroll github page
2.3 Create and setup Router directly on router VM
You can setup the router directly on the router VM with one command if you did not block your controller's edge-management port. At this time, the quickstart for setting up controller does not separate edge-management port from edge-client port, so the edge-management port has to be open. You may continue this section if you know your controller's management password, Fabric Port (default 8440) and Management Port (default 8441).
You can also choose to create router on the controller and then register with the jwt file (created when creating the router) on the router. The procedure for this is detailed in "Create Router On the Controller" section.
2.3.1 Info needed for creating Router
In order to create the Router, the VM needs to contact controller. We need the following information before we can continue:
- Controller IP or Controller NDS
- Controller Fabric Port: On the controller, issue this command echo $ZITI_CTRL_PORT
- Controller Management Port: On the controller, issue this command echo $ZITI_EDGE_CONTROLLER_PORT
- Controller Passwd: On the controller, issue this command echo $ZITI_PWD
- Router Name: Name for this router
2.3.2 Info gathered for creating Router
Here is information I gathered from previous step:
- Controller IP: 68.183.52.206
- Controller Fabric Port: 8440 (default value if following controller setup guide)
- Controller Management Port: 8441 (default value if following controller setup guide)
- Controller Passwd: Test@123
- Router Name: pub-er
We are also going to create the router without healthcheck section and metrics, so the following two options will be used to create the router:
- --disableHealthChecks
- --disableMetrics
If you choose to explore these two functionalities, you can remove the options (from command line) when creating router.
2.3.3 Create the Router with link listener
Use this procedure to create a Public Router with link listener (but without tunnel).
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controller 68.183.52.206 --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --adminUser admin --adminPassword Test@123 --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --routerName pub-er
output
2023-04-05-04:07:44-INFO-Writing jwt file: pub-er_enrollment.jwt
2023-04-05-04:07:44-INFO-Version not specified, going to check with controller
2023-04-05-04:07:45-INFO-Found version 0.27.7
2023-04-05-04:07:45-INFO-Downloading file: https://github.com/openziti/ziti/releases/download/v0.27.7/ziti-linux-amd64-0.27.7.tar.gz
Downloading: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 115M/115M [00:01<00:00, 67.3MiB/s]
2023-04-05-04:07:47-INFO-Successfully downloaded file
2023-04-05-04:07:47-INFO-Starting binary install
2023-04-05-04:07:50-INFO-Installing service unit file
2023-04-05-04:07:50-INFO-Creating config file
2023-04-05-04:07:50-INFO-Starting Router Enrollment
2023-04-05-04:07:54-INFO-Successfully enrolled Ziti
2023-04-05-04:07:54-INFO-Service ziti-router.service start successful.
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ziti-router.service → /etc/systemd/system/ziti-router.service.
2023-04-05-04:07:55-INFO-Service ziti-router.service enable successful.
Alternative way of creating router
Instead of passing parameters through the command line to create routers, the parameters can be specified via environmental variables. Here is example on how to accomplish that.
export CONTROLLER="68.183.52.206"
export CONTROLLERFABRICPORT="8440"
export CONTROLLERMGMTPORT="8441"
export ADMINUSER="admin"
export ADMINPASSWORD="Test@123"
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --routerName pub-er
2.3.4 Other Router creation options
If you need to create router with difference options than the one mentioned above, please choose one of the options from this section.
2.3.4.1 Create the Router with link listener and tunneler
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controller 68.183.52.206 --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --adminUser admin --adminPassword Test@123 --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --autoTunnelListener --routerName pub-er
2.3.4.2 Create the Router with edge listener only (no link listener)
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controller 68.183.52.206 --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --adminUser admin --adminPassword Test@123 --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --routerName pub-er
2.3.4.3 Create the Router with edge listener and tunneler
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controller 68.183.52.206 --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --adminUser admin --adminPassword Test@123 --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --autoTunnelListener --routerName pub-er
2.4 Creating Router on the Controller first
If you already setup the router directly on the VM, you can skip to the next section 2.5
You can create the router on the controller first then register the router on the router VM.
2.4.1 Creating Router on the controller Using ZAC
If you prefer to create router using CLI, you can jump to cli section.
In order to complete the procedures in this section, you need to install ZAC first and have access to the controller using the ZAC. If you have trouble using ZAC, you can use the CLI procedures to create router.
From the ZAC welcome screen, choose the ROUTERS
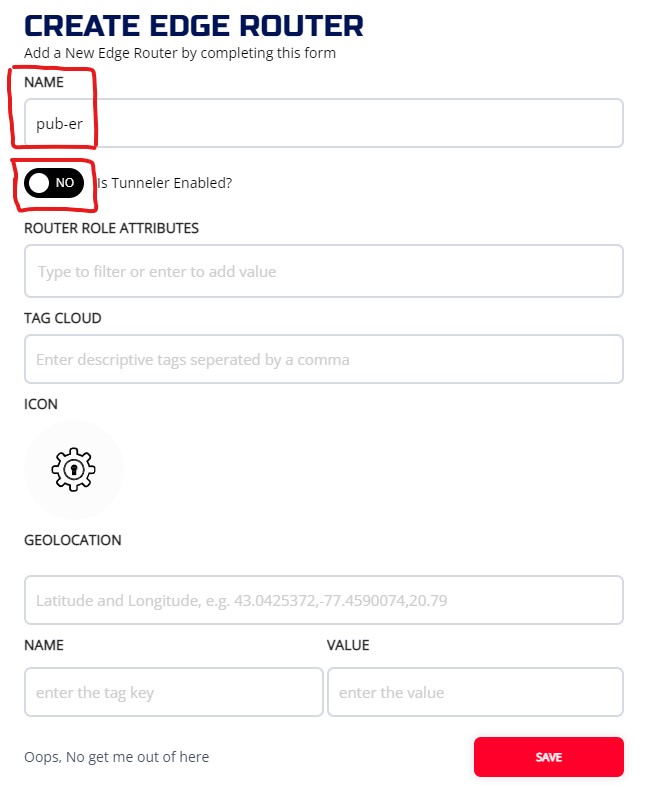
Click on + to bring up the CREATE EDGE ROUTER widget. The NAME of Router is required, and it has to be unique. Also choose whether you want the tunneler to be enable or not on the router. Enter other optional fields and hit SAVE
If the router is created successfully, you will be back to the MANAGE EDGE ROUTERS screen. From the list of edge routers, you will see the JWT icon on the newly created router. You need this JWT for the registration.
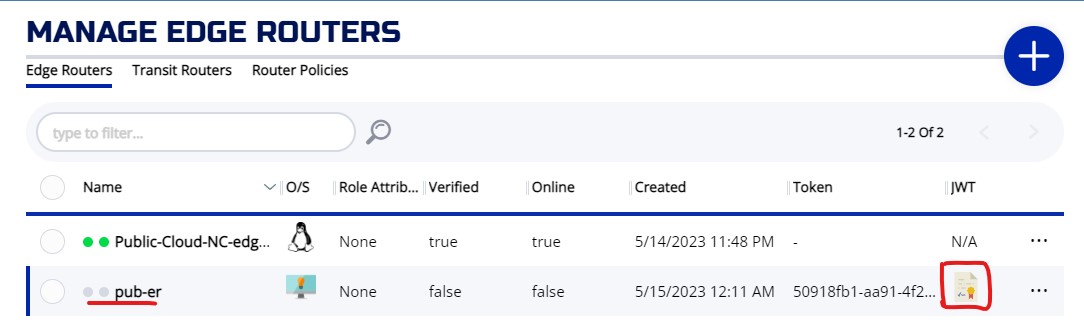
Click on the JWT ICON, the JWT will be downloaded to your machine. On Chrome browser, the downloaded file will appear on the bottom left corner of the browser like picture below.
Open the JWT file, and copy the content. Now you are ready for the registration.

2.4.2 Creating Router on the controller Using CLI
If you already created router using ZAC, you can skip ahead to register the router.
Otherwise, this section provides CLI commands to create routers on the controller.
login to controller
login to CLI first
zitiLogin
To create an edge router (no tunneler)
ziti edge create edge-router pub-er -o pub-er.jwt
output
New edge router pub-er2 created with id: BzUtjC7E.
Enrollment expires at 2023-04-07T03:52:03.997Z
To create an edge router with tunneler
ziti edge create edge-router pub-er -t -o pub-er.jwt
Cat out the content of the jwt file. We will need to use the jwt to register router
# cat pub-er.jwt
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbSI6ImVyb3R0IiwiZXhwIjoxNjgwODM5NjA4LCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovLzE2MS4zNS4xMDguMjE4Ojg0NDEiLCJqdGkiOiJhNDg5N2Q0ZS1lZTY4LTQ1M2UtYjY1NS03MGU0YjgyZTllNDciLCJzdWIiOiJpY2JLakM3RS5QIn0.Y6DohYyWEeJQmRMe29v4cL3Y1APCnBlrv_-S_941au2OESuQdt2CS4C4djvESYzV5vbnbgZgyU5xtNvb4lW5Uv2HP3XUGQNVsWjpwZbazNoTXg1IX6hhWb7T6u1AhS4xnJ3jpoapKsdOkUSqeQNUMSiN3aeLNcGVA_XK1-utCYjVsHDC90M1ZYZqgd8C9IKziDI10XQVlKTqosv8hoJD0OKIu7WZMslweRSMBtQUA2lZ2QSkIhFr2bvtgPll-5aBnG7eo6Ka_WtEW6EikU2fxgpNaVVBEIdZs1tkdGU6dfBDA6j5wA1TBI0FZnuKlNW24bMZCWKy2B_AMqJW1a80I0qNDx-QHEy-pt8FzZ-eqXWyfhc_nYzwT9kr6hO9VJrrD81hboCeTl8G6EXZjwCi2lPbKHROtkQu08-Ns1Kps7R3GILeNMltW9tKApP746ek4DVxm2cKqiB1Axcb0tNjDWTthjyp8m40aSiiqOPIoQbwa43JLqbHcuhZOSBLQNb_bwzkxBSf34D2w5eVETWy9VX-lgHwM-uhT5SfZIWdnWtO7-Cxn-cqgz89twtOim-yc5j0p0ieAbrOArbjKFBXiQjP8yWkorQKlj5PTSk7vyb3X4q6p--RxP2Z5F8alCPQx3XiVcohvIJnrJiEP86myNIYcKhhJ4OB4r9iOr0qTc8
We also need the management port (default 8441) and fabric port (default 8440) of the controller to register the router
# echo $ZITI_EDGE_CONTROLLER_PORT
8441
# echo $ZITI_CTRL_PORT
8440
2.4.3 Register the Router with link listener
Perform this on the Router VM
Use this procedure to create a Public Router with link listener (but without tunnel).
command
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics <jwt content>
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbSI6ImVyb3R0IiwiZXhwIjoxNjgwODM5NjA4LCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovLzE2MS4zNS4xMDguMjE4Ojg0NDEiLCJqdGkiOiJhNDg5N2Q0ZS1lZTY4LTQ1M2UtYjY1NS03MGU0YjgyZTllNDciLCJzdWIiOiJpY2JLakM3RS5QIn0.Y6DohYyWEeJQmRMe29v4cL3Y1APCnBlrv_-S_941au2OESuQdt2CS4C4djvESYzV5vbnbgZgyU5xtNvb4lW5Uv2HP3XUGQNVsWjpwZbazNoTXg1IX6hhWb7T6u1AhS4xnJ3jpoapKsdOkUSqeQNUMSiN3aeLNcGVA_XK1-utCYjVsHDC90M1ZYZqgd8C9IKziDI10XQVlKTqosv8hoJD0OKIu7WZMslweRSMBtQUA2lZ2QSkIhFr2bvtgPll-5aBnG7eo6Ka_WtEW6EikU2fxgpNaVVBEIdZs1tkdGU6dfBDA6j5wA1TBI0FZnuKlNW24bMZCWKy2B_AMqJW1a80I0qNDx-QHEy-pt8FzZ-eqXWyfhc_nYzwT9kr6hO9VJrrD81hboCeTl8G6EXZjwCi2lPbKHROtkQu08-Ns1Kps7R3GILeNMltW9tKApP746ek4DVxm2cKqiB1Axcb0tNjDWTthjyp8m40aSiiqOPIoQbwa43JLqbHcuhZOSBLQNb_bwzkxBSf34D2w5eVETWy9VX-lgHwM-uhT5SfZIWdnWtO7-Cxn-cqgz89twtOim-yc5j0p0ieAbrOArbjKFBXiQjP8yWkorQKlj5PTSk7vyb3X4q6p--RxP2Z5F8alCPQx3XiVcohvIJnrJiEP86myNIYcKhhJ4OB4r9iOr0qTc8
output
2023-04-07-01:07:49-INFO-Version not specified, going to check with controller
2023-04-07-01:07:49-INFO-Found version 0.27.7
2023-04-07-01:07:49-INFO-Downloading file: https://github.com/openziti/ziti/releases/download/v0.27.7/ziti-linux-amd64-0.27.7.tar.gz
Downloading: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 115M/115M [00:01<00:00, 68.9MiB/s]
2023-04-07-01:07:51-INFO-Successfully downloaded file
2023-04-07-01:07:51-INFO-Starting binary install
2023-04-07-01:07:54-INFO-Installing service unit file
2023-04-07-01:07:55-INFO-Service ziti-router daemon-reload successful.
2023-04-07-01:07:55-INFO-Creating config file
2023-04-07-01:07:55-INFO-Starting Router Enrollment
2023-04-07-01:07:57-INFO-Successfully enrolled Ziti
2023-04-07-01:07:57-INFO-Service ziti-router.service start successful.
2023-04-07-01:07:57-INFO-Service ziti-router.service enable successful.
2.4.4 Other Router creation options
If you need to create router with difference options than the one mentioned above, please choose one of the options from this section.
2.4.4.1 Register the Router with link listener and tunneler
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --assumePublic --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --autoTunnelListener <jwt content>
2.4.4.2 Register the Router with edge listener only (no link listener)
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics <jwt content>
2.4.4.3 Register the Router with edge listener and tunneler
sudo ./ziti_router_auto_enroll -f -n --controllerFabricPort 8440 --controllerMgmtPort 8441 --disableHealthChecks --disableMetrics --autoTunnelListener <jwt content>
2.5 Auto start the router
After enroll the router, a systemd service file is automatically created and enabled. To check the status of the service file, issue the following command:
systemctl status ziti-router
Output
● ziti-router.service - Ziti-Router
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/ziti-router.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-04-05 14:45:59 UTC; 4s ago
Main PID: 18381 (ziti)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2323)
Memory: 16.5M
CPU: 222ms
CGroup: /system.slice/ziti-router.service
└─18381 /opt/ziti/ziti router run /opt/ziti/config.yaml
If the status shows active (running), then the setup finished correctly.
On the controller, you can check the status of the routers. Please refer to the controller guide (useful command for the Router) section for more information.
2.7 Route Table
- Azure
- AWS
- Google Cloud
For any router setup as local gateway (i.e. local-er in test network 2), you will need to setup routes in Azure.
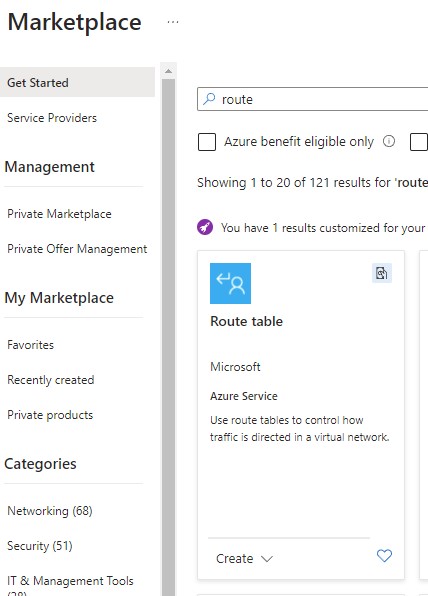
First you need to create a Route Table from Marketplace.
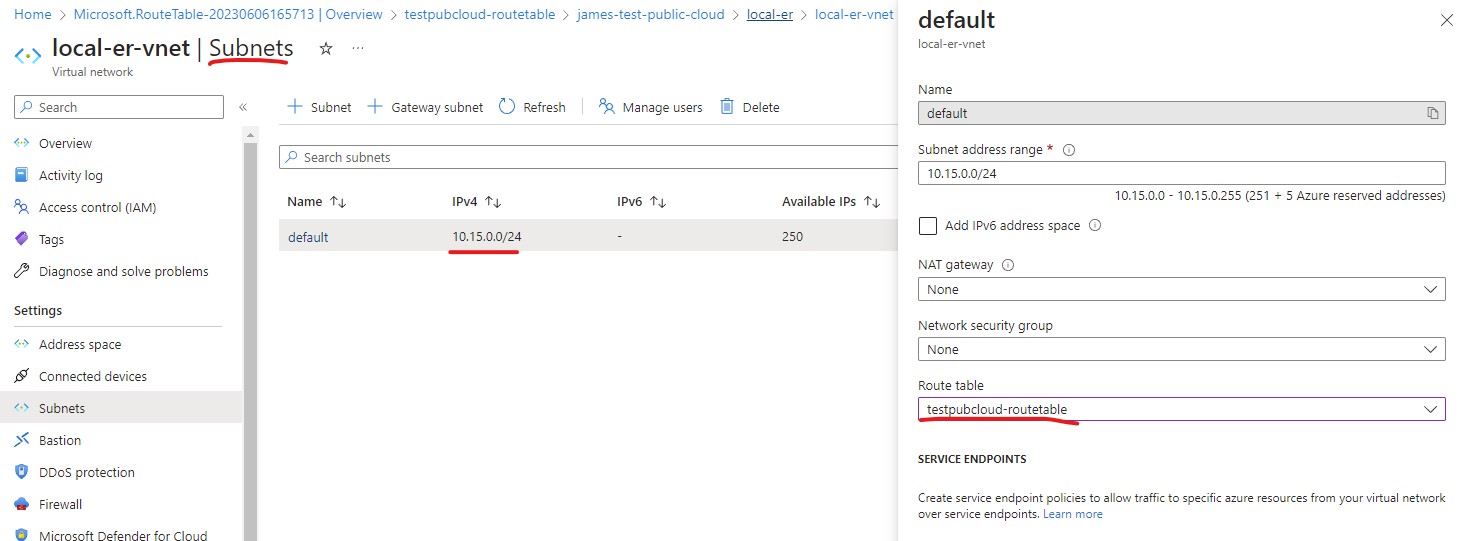
Then go to your subnet of your VM, associate the Route Table just created to the subnet.
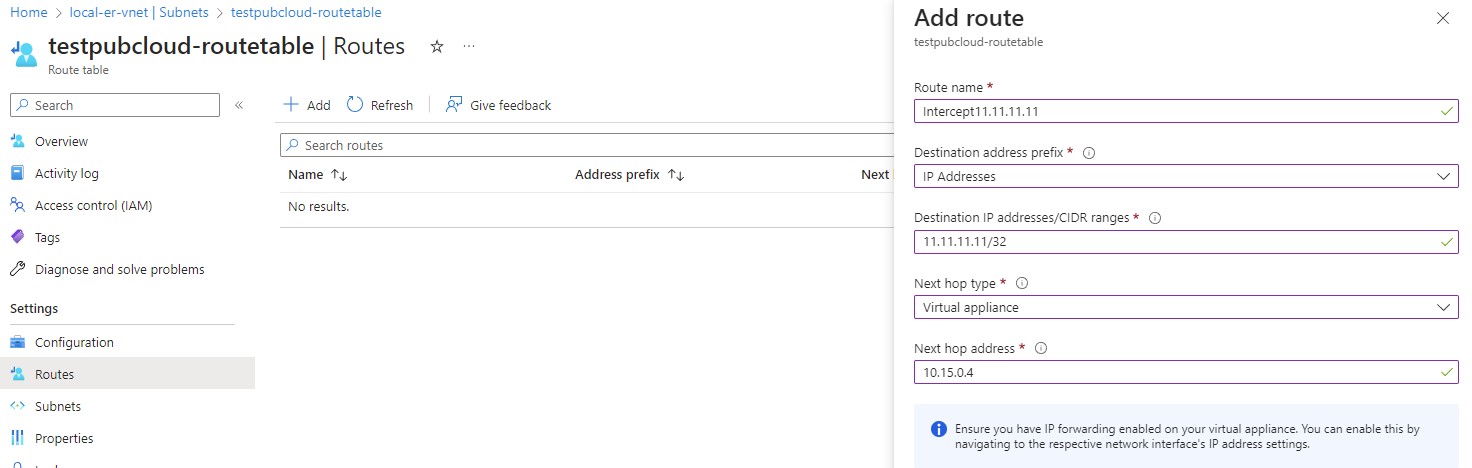
Click on the route table, then choose Routes from the left side menu.
Now you will be presented a screen like below, you can then add your route.
Following is an example route for intercepting traffic destine for ip: 11.11.11.11/32.
The Next hop address is local IP of our local gateway ER.
The following routes are required:
- any intercept address cidr
- 100.64.0.0/10 (for DNS based intercept)
- For any router setup as local gateway (i.e. local-er in test network 2), you will need to setup routes for your VPC.
- To get to the route table, click on Subnet from your Instances screen
- From the Subnet screen, click on Router table
- Then you can use Edit routes to add routes to the table.
- Following is an example routes for intercepting traffic destine for IP subnet: 10.10.0.0/24 and 100.64.0.1/32.
- The Target is Instance (our local gateway ER).
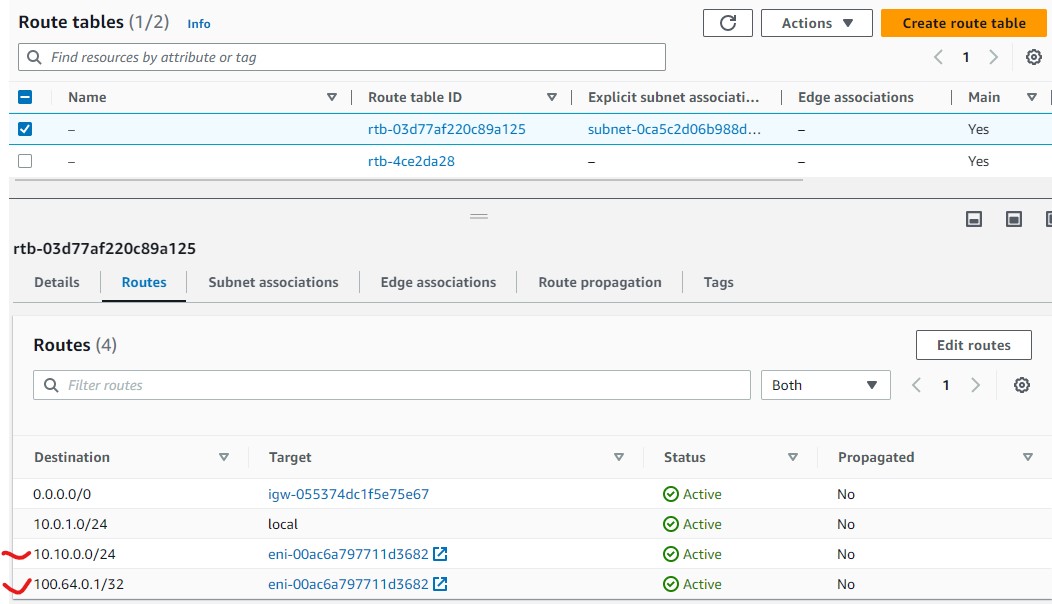
The following routes are required:
- any intercept address CIDR
- 100.64.0.0/10 (for DNS based intercept)
For any router setup as local gateway (i.e. local-er in test network 2), you will need to setup routes in GCP.
- Go to your VM screen, click on the Network interfaces name (i.e. nic0)
- Click on Routes menu on the left side to bring up the Routes screen
- Click ROUTE MANAGEMENT and + CREATE ROUTE to bring up a dialog to create a route
- Specify your Network and Destination IP range
- Next hop is our local-er instance.
- Click CREATE to generate the route.
Following is an example route for intercepting traffic destine for ip: 11.11.11.11/32. The next hop is our local gateway ER.
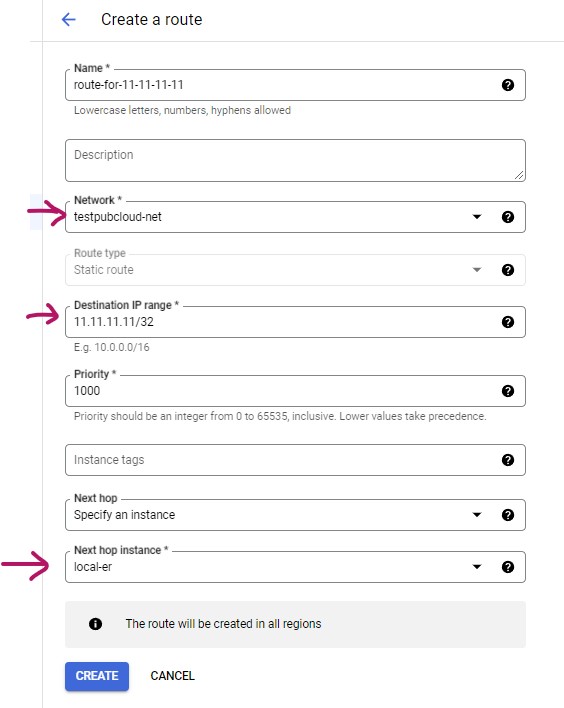
The following routes are required:
- any intercept address CIDR
- 100.64.0.0/10 (for DNS based intercept)
2.8 Source and Destination Check
Most cloud provider checks the source and destination of the traffic to make sure it is either originated or terminated at the VM. When our ER is used as a local GW, it is neither the source or the destination of the traffic. Therefore, the source and destination check must be disabled.
- Azure
- AWS
- Google Cloud
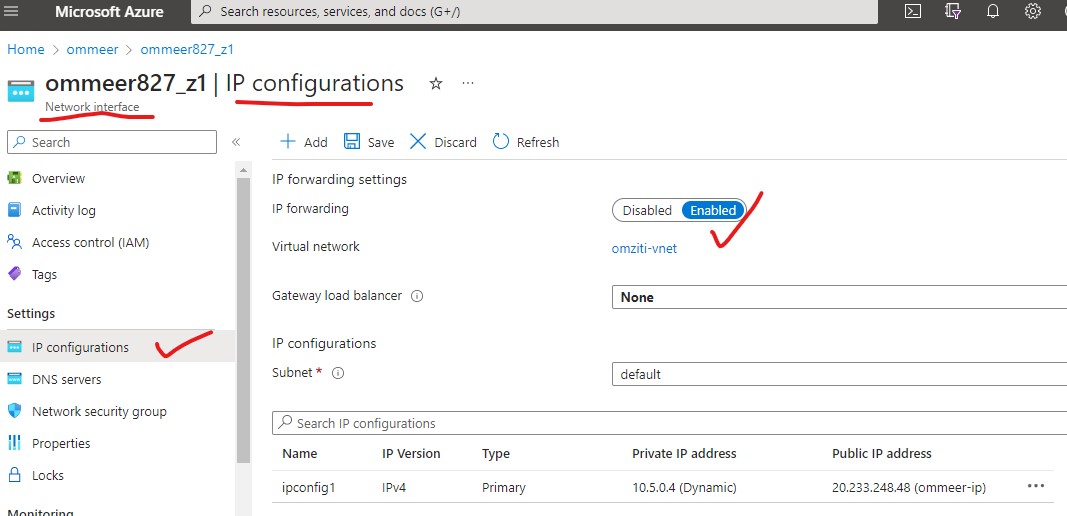
- In Azure, the "Source and Destination Check" is called IP forwarding
- From your Virtual machine screen, click on the Network Interface of that VM.
- On the left side menu, choose IP configurations (like the picture below).
- Enable the IP forwarding
- Save
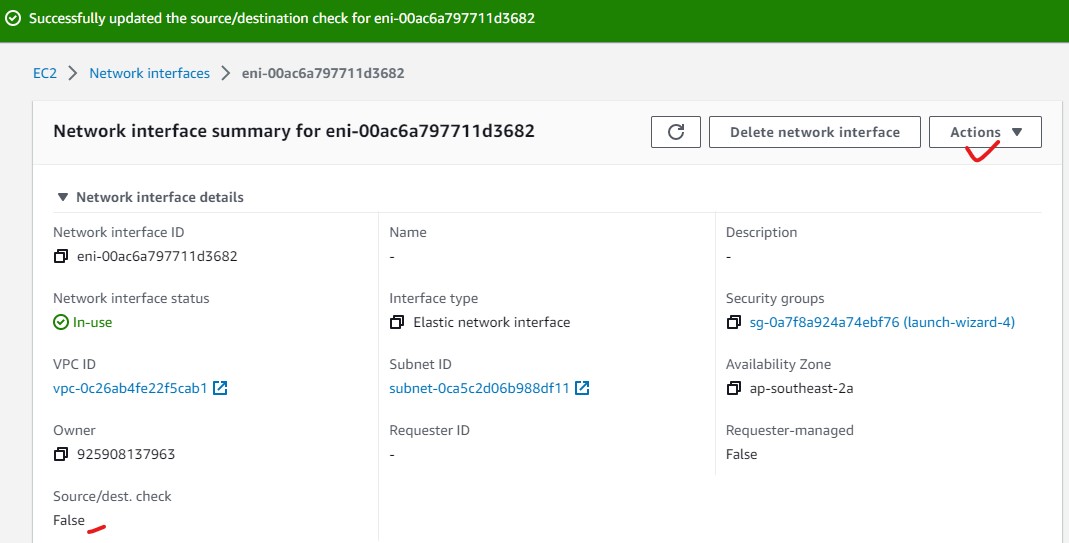
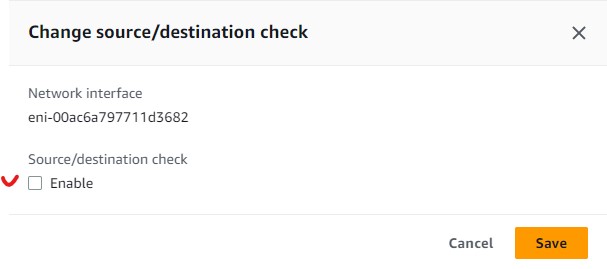
- From your Instance screen, Under Networking tab, click on the Network Interface of that VM.
- Click on Actions on the right side to bring up a dropdown menu.
- Select Change source/dest. check
- uncheck Enable and then press Save
In GCP, the "Source and Destination Check" is named IP forwarding
During the VM creation, from the VM configuration screen, choose the ADVANCED OPTIONS & under the NETWORKING section (like the picture below). Enable the IP forwarding
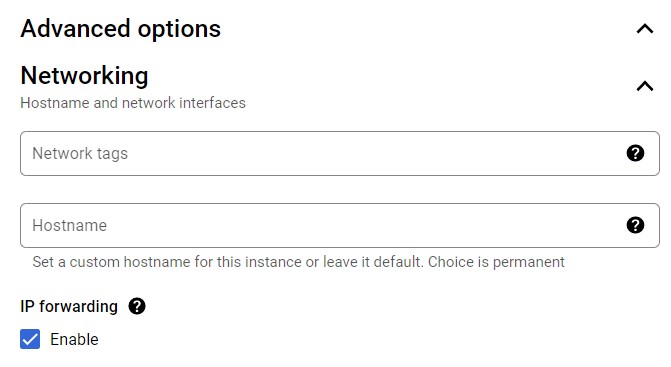
If the IP forwarding was not enabled during VM creation, you can follow this procedure to enable it.
2.9 Firewall
- Azure
- AWS
- Google Cloud
Azure's default firewall is blocking all incoming access to the VM. You will need the following ports open for your ERs:
- 443/TCP (default port for edge listener)
- 80/TCP (default port for link listener)
- 53/UDP (when using as local gw)
- any intercept ports. (i.e. if you want to intercept RDP traffic, you will need to open port 3389)
To open ports:
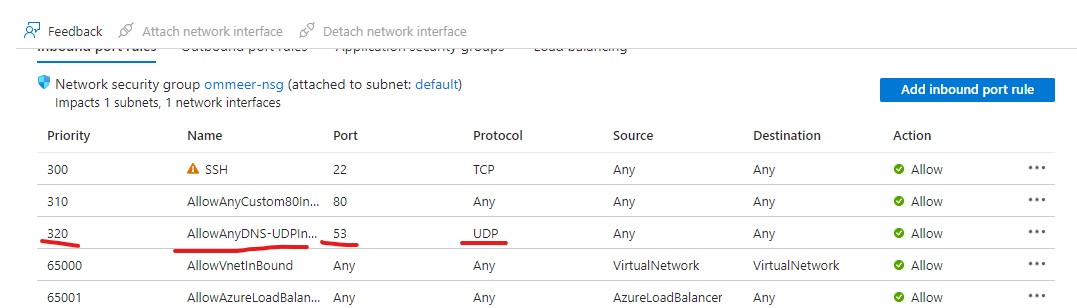
- From your Virtual machine page, click on Networking from the left side menu.
- Under the Inbound port rules, you can click on Add inbound port rule to allow traffic in. Like example here.
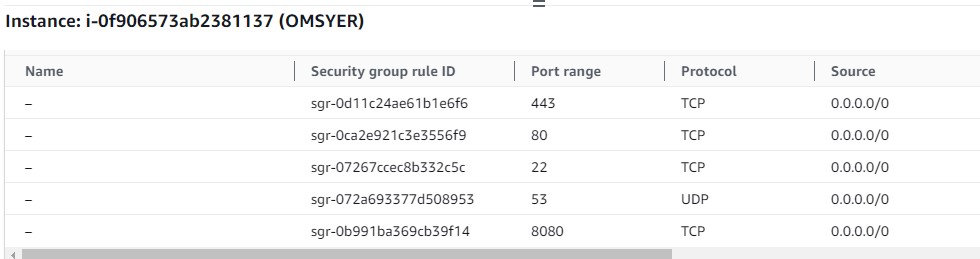
AWS default firewall is blocking all incoming access to the VM. You will need the following ports open for your ERs:
- 443/TCP (default port for edge listener)
- 80/TCP (default port for link listener)
- 53/UDP (when using as local gw)
- any intercept ports. (i.e. if you want to intercept RDP traffic, you will need to open port 3389)
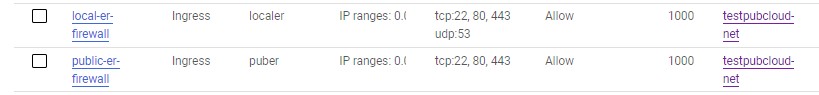
Following is the firewall setting for edge router which serves as the GW for non ziti client.
GCP default firewall is blocking all incoming access to the VM. You will need the following ports open for your ERs:
- 443/TCP (default port for edge listener)
- 80/TCP (default port for link listener)
- 53/UDP (when using as local gw)
- any intercept ports. (i.e. if you want to intercept RDP traffic, you will need to open port 3389)
Following is example firewall configuration for public ER and local ER.